Book an Appointment
Treatment of Overactive Bladder
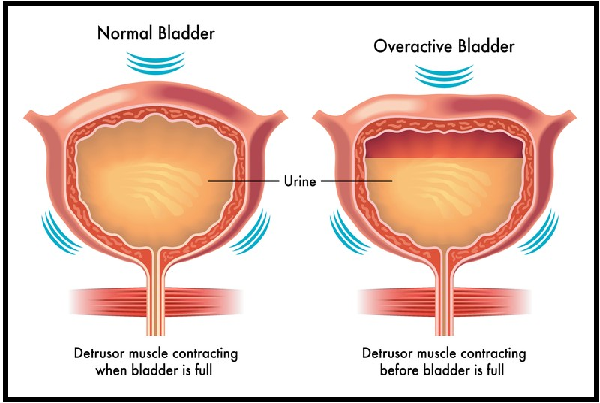
Treatment of Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a medical condition characterized by a group of urinary symptoms that result from involuntary contractions of the muscles in the bladder wall. These contractions create a sudden, urgent need to urinate, often leading to frequent urination and, in some cases, urinary incontinence. Overactive bladder can significantly impact a person's quality of life and daily activities.
Common Symptoms of Overactive Bladder:
- Urgency: A sudden, compelling need to urinate that is difficult to control.
- Frequency: Urinating more often than normal, typically defined as eight or more times in a 24-hour period.
- Nocturia: Waking up at night to urinate.
- Urge Incontinence: The involuntary loss of urine associated with a strong urge to void.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause of overactive bladder is not always clear, but several factors may contribute to its development:
-
Age: OAB becomes more common as people age, with prevalence increasing with advancing age.
-
Gender: Women are more likely than men to experience overactive bladder, particularly after menopause.
-
Bladder Conditions: Conditions such as bladder stones or urinary tract infections can contribute to OAB symptoms.
-
Neurological Disorders: Conditions affecting the nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis or stroke, may disrupt normal bladder function.
-
Bladder Obstruction: An obstruction or blockage in the bladder or urinary tract can lead to OAB symptoms.
-
Medications: Some medications can contribute to urinary symptoms.
-
Bladder Muscle Changes: Changes in the muscles of the bladder, which may occur with age, can contribute to OAB.
Get In Touch
Tags
- urologist in karol bagh
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist in karol bagh
- Best urologist in Karol Bagh
- Best andrologist in Karol Bagh
- Best urology doctor in Karol Bagh
- Best andrology doctor in Karol Bagh
- Best andrology treatment in Karol Bagh
- Best urology treatment in Karol Bagh
- Urologist treatment specialist in Karol Bagh
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Karol Bagh
- Circumcision treatment in Karol Bagh
- Flexible cystoscopy in Karol Bagh
- Vasectomy surgery in Karol Bagh
- Prostate biopsy in Karol Bagh
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Karol Bagh
- OIU for stricture urethra in Karol Bagh
- Laser renal stone surgery in Karol Bagh
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Karol Bagh
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Karol Bagh
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Karol Bagh
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Karol Bagh
- Kidney stone treatment in Karol Bagh
- RIRS surgery in Karol Bagh
- PCNL surgery in Karol Bagh
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Karol Bagh
- TURP surgery in Karol Bagh
- HoLEP surgery in Karol Bagh
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Karol Bagh
- TURBT surgery in Karol Bagh
- Prostate cancer treatment in Karol Bagh
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Karol Bagh
- Overactive bladder treatment in Karol Bagh
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Karol Bagh
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Karol Bagh
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Karol Bagh
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Karol Bagh
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Karol Bagh
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Karol Bagh
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Karol Bagh
- Testicular biopsy in Karol Bagh
- Micro TESE treatment in Karol Bagh
- Testicular biopsy in Karol Bagh
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Karol Bagh
- Best urologist in Patel Nagar
- Best andrologist in Patel Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Patel Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Patel Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Patel Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Patel Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Patel Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Patel Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Patel Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Patel Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Patel Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Patel Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Patel Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Patel Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Patel Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Patel Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Patel Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Patel Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Patel Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Patel Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Patel Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Patel Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Patel Nagar
- TURP surgery in Patel Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Patel Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Patel Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Patel Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Patel Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Patel Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Patel Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Patel Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Patel Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Patel Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Patel Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Patel Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Patel Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Patel Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Patel Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Patel Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Patel Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Patel Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Patel Nagar
- Best urologist in Kirti Nagar
- Best andrologist in Kirti Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Kirti Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Kirti Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Kirti Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Kirti Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Kirti Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Kirti Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Kirti Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Kirti Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Kirti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Kirti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Kirti Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Kirti Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Kirti Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Kirti Nagar
- TURP surgery in Kirti Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Kirti Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Kirti Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Kirti Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Kirti Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Kirti Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Kirti Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Kirti Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Kirti Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Kirti Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Best urologist in Moti Nagar
- Best andrologist in Moti Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Moti Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Moti Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Moti Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Moti Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Moti Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Moti Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Moti Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Moti Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Moti Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Moti Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Moti Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Moti Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Moti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Moti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Moti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Moti Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Moti Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Moti Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Moti Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Moti Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Moti Nagar
- TURP surgery in Moti Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Moti Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Moti Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Moti Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Moti Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Moti Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Moti Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Moti Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Moti Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Moti Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Moti Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Moti Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Moti Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Moti Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Moti Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Moti Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Moti Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Moti Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Moti Nagar
- Best urologist in Keshav Puram
- Best andrologist in Keshav Puram
- Best urology doctor in Keshav Puram
- Best andrology doctor in Keshav Puram
- Best andrology treatment in Keshav Puram
- Best urology treatment in Keshav Puram
- Urologist treatment specialist in Keshav Puram
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Keshav Puram
- Circumcision treatment in Keshav Puram
- Flexible cystoscopy in Keshav Puram
- Vasectomy surgery in Keshav Puram
- Prostate biopsy in Keshav Puram
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Keshav Puram
- OIU for stricture urethra in Keshav Puram
- Laser renal stone surgery in Keshav Puram
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Keshav Puram
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Keshav Puram
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Keshav Puram
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Keshav Puram
- Kidney stone treatment in Keshav Puram
- RIRS surgery in Keshav Puram
- PCNL surgery in Keshav Puram
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Keshav Puram
- TURP surgery in Keshav Puram
- HoLEP surgery in Keshav Puram
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Keshav Puram
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Keshav Puram
- TURBT surgery in Keshav Puram
- Prostate cancer treatment in Keshav Puram
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Keshav Puram
- Overactive bladder treatment in Keshav Puram
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Keshav Puram
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Keshav Puram
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Keshav Puram
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Keshav Puram
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Keshav Puram
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Keshav Puram
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Keshav Puram
- Testicular biopsy in Keshav Puram
- Micro TESE treatment in Keshav Puram
- Testicular biopsy in Keshav Puram
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Keshav Puram
- Best urologist in Ashok Vihar
- Best andrologist in Ashok Vihar
- Best urology doctor in Ashok Vihar
- Best andrology doctor in Ashok Vihar
- Best andrology treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Best urology treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Ashok Vihar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Ashok Vihar
- Circumcision treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Ashok Vihar
- Vasectomy surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Prostate biopsy in Ashok Vihar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Ashok Vihar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Ashok Vihar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Ashok Vihar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Ashok Vihar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Ashok Vihar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Kidney stone treatment in Ashok Vihar
- RIRS surgery in Ashok Vihar
- PCNL surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Ashok Vihar
- TURP surgery in Ashok Vihar
- HoLEP surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Ashok Vihar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Ashok Vihar
- TURBT surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Ashok Vihar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Ashok Vihar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Ashok Vihar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Ashok Vihar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Ashok Vihar
- Testicular biopsy in Ashok Vihar
- Micro TESE treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Testicular biopsy in Ashok Vihar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Best urologist in Shadipur
- Best andrologist in Shadipur
- Best urology doctor in Shadipur
- Best andrology doctor in Shadipur
- Best andrology treatment in Shadipur
- Best urology treatment in Shadipur
- Urologist treatment specialist in Shadipur
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Shadipur
- Circumcision treatment in Shadipur
- Flexible cystoscopy in Shadipur
- Vasectomy surgery in Shadipur
- Prostate biopsy in Shadipur
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Shadipur
- OIU for stricture urethra in Shadipur
- Laser renal stone surgery in Shadipur
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Shadipur
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Shadipur
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Shadipur
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Shadipur
- Kidney stone treatment in Shadipur
- RIRS surgery in Shadipur
- PCNL surgery in Shadipur
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Shadipur
- TURP surgery in Shadipur
- HoLEP surgery in Shadipur
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Shadipur
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Shadipur
- TURBT surgery in Shadipur
- Prostate cancer treatment in Shadipur
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Shadipur
- Overactive bladder treatment in Shadipur
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Shadipur
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Shadipur
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Shadipur
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Shadipur
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Shadipur
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Shadipur
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Shadipur
- Testicular biopsy in Shadipur
- Micro TESE treatment in Shadipur
- Testicular biopsy in Shadipur
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Shadipur
- Best urologist in Paharganj
- Best andrologist in Paharganj
- Best urology doctor in Paharganj
- Best andrology doctor in Paharganj
- Best andrology treatment in Paharganj
- Best urology treatment in Paharganj
- Urologist treatment specialist in Paharganj
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Paharganj
- Circumcision treatment in Paharganj
- Flexible cystoscopy in Paharganj
- Vasectomy surgery in Paharganj
- Prostate biopsy in Paharganj
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Paharganj
- OIU for stricture urethra in Paharganj
- Laser renal stone surgery in Paharganj
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Paharganj
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Paharganj
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Paharganj
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Paharganj
- Kidney stone treatment in Paharganj
- RIRS surgery in Paharganj
- PCNL surgery in Paharganj
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Paharganj
- TURP surgery in Paharganj
- HoLEP surgery in Paharganj
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Paharganj
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Paharganj
- TURBT surgery in Paharganj
- Prostate cancer treatment in Paharganj
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Paharganj
- Overactive bladder treatment in Paharganj
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Paharganj
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Paharganj
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Paharganj
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Paharganj
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Paharganj
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Paharganj
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Paharganj
- Testicular biopsy in Paharganj
- Micro TESE treatment in Paharganj
- Testicular biopsy in Paharganj
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Paharganj
- Best urologist in Rajouri Garden
- Best andrologist in Rajouri Garden
- Best urology doctor in Rajouri Garden
- Best andrology doctor in Rajouri Garden
- Best andrology treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Best urology treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Urologist treatment specialist in Rajouri Garden
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Rajouri Garden
- Circumcision treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Flexible cystoscopy in Rajouri Garden
- Vasectomy surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Prostate biopsy in Rajouri Garden
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Rajouri Garden
- OIU for stricture urethra in Rajouri Garden
- Laser renal stone surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Rajouri Garden
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Rajouri Garden
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Rajouri Garden
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Kidney stone treatment in Rajouri Garden
- RIRS surgery in Rajouri Garden
- PCNL surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Rajouri Garden
- TURP surgery in Rajouri Garden
- HoLEP surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Rajouri Garden
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Rajouri Garden
- TURBT surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Prostate cancer treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Rajouri Garden
- Overactive bladder treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Rajouri Garden
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Rajouri Garden
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Rajouri Garden
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Rajouri Garden
- Testicular biopsy in Rajouri Garden
- Micro TESE treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Testicular biopsy in Rajouri Garden
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Best urologist in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best andrologist in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Kanhaiya Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Kanhaiya Nagar
- TURP surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best urologist in Shastri Nagar
- Best andrologist in Shastri Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Shastri Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Shastri Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Shastri Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Shastri Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Shastri Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Shastri Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Shastri Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Shastri Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Shastri Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Shastri Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Shastri Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Shastri Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Shastri Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Shastri Nagar
- TURP surgery in Shastri Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Shastri Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Shastri Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Shastri Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Shastri Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Shastri Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Shastri Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Shastri Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Shastri Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Shastri Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Shastri Nagar
- urologist in Rajinder Nagar
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist in Rajinder Nagar
- Best urologist in Rajinder Nagar
- Best andrologist in Rajinder Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Rajinder Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Rajinder Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Rajinder Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Rajinder Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Rajinder Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Rajinder Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Rajinder Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Rajinder Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Rajinder Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Rajinder Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Rajinder Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Rajinder Nagar
- TURP surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Rajinder Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Rajinder Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Rajinder Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Rajinder Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Rajinder Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Rajinder Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Rajinder Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- urologist in Rajendra Place
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist in Rajendra Place
- Best urologist in Rajendra Place
- Best andrologist in Rajendra Place
- Best urology doctor in Rajendra Place
- Best andrology doctor in Rajendra Place
- Best andrology treatment in Rajendra Place
- Best urology treatment in Rajendra Place
- Urologist treatment specialist in Rajendra Place
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Rajendra Place
- Circumcision treatment in Rajendra Place
- Flexible cystoscopy in Rajendra Place
- Vasectomy surgery in Rajendra Place
- Prostate biopsy in Rajendra Place
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Rajendra Place
- OIU for stricture urethra in Rajendra Place
- Laser renal stone surgery in Rajendra Place
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Rajendra Place
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Rajendra Place
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Rajendra Place
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Rajendra Place
- Kidney stone treatment in Rajendra Place
- RIRS surgery in Rajendra Place
- PCNL surgery in Rajendra Place
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Rajendra Place
- TURP surgery in Rajendra Place
- HoLEP surgery in Rajendra Place
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Rajendra Place
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Rajendra Place
- TURBT surgery in Rajendra Place
- Prostate cancer treatment in Rajendra Place
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Rajendra Place
- Overactive bladder treatment in Rajendra Place
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Rajendra Place
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Rajendra Place
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Rajendra Place
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Rajendra Place
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Rajendra Place
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Rajendra Place
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Rajendra Place
- Testicular biopsy in Rajendra Place
- Micro TESE treatment in Rajendra Place
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Rajendra Place
- show more
- show less






