Book an Appointment
AV Fistula for Hemodialysis
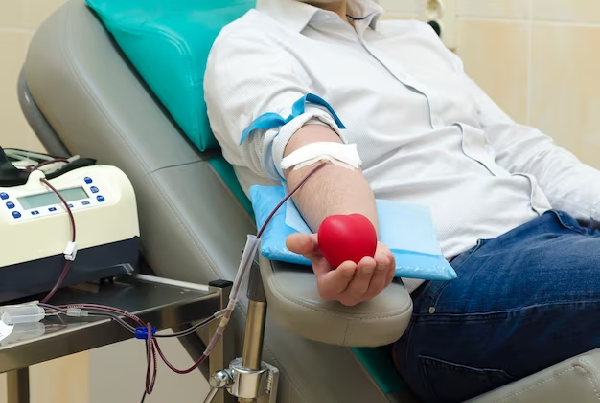
AV Fistula for Hemodialysis
An AV (arteriovenous) fistula is a surgically created connection between an artery and a vein, typically in the arm, for the purpose of facilitating hemodialysis. This vascular access is crucial for individuals with kidney failure who require regular hemodialysis treatments.
-
Creation: During the AV fistula procedure, a surgeon connects an artery to a nearby vein, creating a direct pathway for blood flow. This connection allows the vein to enlarge and become more robust, providing easier access for repeated needle insertions required during hemodialysis.
-
Maturation: It takes time for the AV fistula to mature and become suitable for dialysis. This process involves the vein becoming larger and developing a stronger blood flow, making it durable for the high-volume blood circulation required during hemodialysis.
-
Hemodialysis Access: Once matured, the AV fistula serves as a reliable and long-lasting access point for hemodialysis. During each dialysis session, needles are inserted into the fistula to allow blood to flow from the patient's body to the dialysis machine, where it is cleaned and filtered before returning to the body.
-
Advantages: AV fistulas are preferred for hemodialysis because they have a lower risk of infection and complications compared to other types of vascular access. They also tend to have better blood flow rates, making hemodialysis sessions more efficient.
-
Care: Proper care and monitoring of the AV fistula, such as avoiding constriction or compression, are essential to maintain its function and prevent complications.
Having a well-functioning AV fistula is crucial for the success of hemodialysis treatments, and it is considered the preferred method of vascular access for long-term hemodialysis patients.
Get In Touch
Tags
- urologist in karol bagh
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist in karol bagh
- Best urologist in Karol Bagh
- Best andrologist in Karol Bagh
- Best urology doctor in Karol Bagh
- Best andrology doctor in Karol Bagh
- Best andrology treatment in Karol Bagh
- Best urology treatment in Karol Bagh
- Urologist treatment specialist in Karol Bagh
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Karol Bagh
- Circumcision treatment in Karol Bagh
- Flexible cystoscopy in Karol Bagh
- Vasectomy surgery in Karol Bagh
- Prostate biopsy in Karol Bagh
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Karol Bagh
- OIU for stricture urethra in Karol Bagh
- Laser renal stone surgery in Karol Bagh
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Karol Bagh
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Karol Bagh
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Karol Bagh
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Karol Bagh
- Kidney stone treatment in Karol Bagh
- RIRS surgery in Karol Bagh
- PCNL surgery in Karol Bagh
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Karol Bagh
- TURP surgery in Karol Bagh
- HoLEP surgery in Karol Bagh
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Karol Bagh
- TURBT surgery in Karol Bagh
- Prostate cancer treatment in Karol Bagh
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Karol Bagh
- Overactive bladder treatment in Karol Bagh
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Karol Bagh
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Karol Bagh
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Karol Bagh
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Karol Bagh
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Karol Bagh
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Karol Bagh
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Karol Bagh
- Testicular biopsy in Karol Bagh
- Micro TESE treatment in Karol Bagh
- Testicular biopsy in Karol Bagh
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Karol Bagh
- Best urologist in Patel Nagar
- Best andrologist in Patel Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Patel Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Patel Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Patel Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Patel Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Patel Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Patel Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Patel Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Patel Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Patel Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Patel Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Patel Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Patel Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Patel Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Patel Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Patel Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Patel Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Patel Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Patel Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Patel Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Patel Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Patel Nagar
- TURP surgery in Patel Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Patel Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Patel Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Patel Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Patel Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Patel Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Patel Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Patel Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Patel Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Patel Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Patel Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Patel Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Patel Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Patel Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Patel Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Patel Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Patel Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Patel Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Patel Nagar
- Best urologist in Kirti Nagar
- Best andrologist in Kirti Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Kirti Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Kirti Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Kirti Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Kirti Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Kirti Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Kirti Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Kirti Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Kirti Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Kirti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Kirti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Kirti Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Kirti Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Kirti Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Kirti Nagar
- TURP surgery in Kirti Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Kirti Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Kirti Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Kirti Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Kirti Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Kirti Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Kirti Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Kirti Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Kirti Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Kirti Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Kirti Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Kirti Nagar
- Best urologist in Moti Nagar
- Best andrologist in Moti Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Moti Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Moti Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Moti Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Moti Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Moti Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Moti Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Moti Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Moti Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Moti Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Moti Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Moti Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Moti Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Moti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Moti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Moti Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Moti Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Moti Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Moti Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Moti Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Moti Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Moti Nagar
- TURP surgery in Moti Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Moti Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Moti Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Moti Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Moti Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Moti Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Moti Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Moti Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Moti Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Moti Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Moti Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Moti Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Moti Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Moti Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Moti Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Moti Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Moti Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Moti Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Moti Nagar
- Best urologist in Keshav Puram
- Best andrologist in Keshav Puram
- Best urology doctor in Keshav Puram
- Best andrology doctor in Keshav Puram
- Best andrology treatment in Keshav Puram
- Best urology treatment in Keshav Puram
- Urologist treatment specialist in Keshav Puram
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Keshav Puram
- Circumcision treatment in Keshav Puram
- Flexible cystoscopy in Keshav Puram
- Vasectomy surgery in Keshav Puram
- Prostate biopsy in Keshav Puram
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Keshav Puram
- OIU for stricture urethra in Keshav Puram
- Laser renal stone surgery in Keshav Puram
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Keshav Puram
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Keshav Puram
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Keshav Puram
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Keshav Puram
- Kidney stone treatment in Keshav Puram
- RIRS surgery in Keshav Puram
- PCNL surgery in Keshav Puram
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Keshav Puram
- TURP surgery in Keshav Puram
- HoLEP surgery in Keshav Puram
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Keshav Puram
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Keshav Puram
- TURBT surgery in Keshav Puram
- Prostate cancer treatment in Keshav Puram
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Keshav Puram
- Overactive bladder treatment in Keshav Puram
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Keshav Puram
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Keshav Puram
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Keshav Puram
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Keshav Puram
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Keshav Puram
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Keshav Puram
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Keshav Puram
- Testicular biopsy in Keshav Puram
- Micro TESE treatment in Keshav Puram
- Testicular biopsy in Keshav Puram
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Keshav Puram
- Best urologist in Ashok Vihar
- Best andrologist in Ashok Vihar
- Best urology doctor in Ashok Vihar
- Best andrology doctor in Ashok Vihar
- Best andrology treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Best urology treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Ashok Vihar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Ashok Vihar
- Circumcision treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Ashok Vihar
- Vasectomy surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Prostate biopsy in Ashok Vihar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Ashok Vihar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Ashok Vihar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Ashok Vihar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Ashok Vihar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Ashok Vihar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Kidney stone treatment in Ashok Vihar
- RIRS surgery in Ashok Vihar
- PCNL surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Ashok Vihar
- TURP surgery in Ashok Vihar
- HoLEP surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Ashok Vihar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Ashok Vihar
- TURBT surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Ashok Vihar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Ashok Vihar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Ashok Vihar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Ashok Vihar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Ashok Vihar
- Testicular biopsy in Ashok Vihar
- Micro TESE treatment in Ashok Vihar
- Testicular biopsy in Ashok Vihar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Ashok Vihar
- Best urologist in Shadipur
- Best andrologist in Shadipur
- Best urology doctor in Shadipur
- Best andrology doctor in Shadipur
- Best andrology treatment in Shadipur
- Best urology treatment in Shadipur
- Urologist treatment specialist in Shadipur
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Shadipur
- Circumcision treatment in Shadipur
- Flexible cystoscopy in Shadipur
- Vasectomy surgery in Shadipur
- Prostate biopsy in Shadipur
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Shadipur
- OIU for stricture urethra in Shadipur
- Laser renal stone surgery in Shadipur
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Shadipur
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Shadipur
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Shadipur
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Shadipur
- Kidney stone treatment in Shadipur
- RIRS surgery in Shadipur
- PCNL surgery in Shadipur
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Shadipur
- TURP surgery in Shadipur
- HoLEP surgery in Shadipur
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Shadipur
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Shadipur
- TURBT surgery in Shadipur
- Prostate cancer treatment in Shadipur
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Shadipur
- Overactive bladder treatment in Shadipur
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Shadipur
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Shadipur
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Shadipur
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Shadipur
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Shadipur
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Shadipur
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Shadipur
- Testicular biopsy in Shadipur
- Micro TESE treatment in Shadipur
- Testicular biopsy in Shadipur
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Shadipur
- Best urologist in Paharganj
- Best andrologist in Paharganj
- Best urology doctor in Paharganj
- Best andrology doctor in Paharganj
- Best andrology treatment in Paharganj
- Best urology treatment in Paharganj
- Urologist treatment specialist in Paharganj
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Paharganj
- Circumcision treatment in Paharganj
- Flexible cystoscopy in Paharganj
- Vasectomy surgery in Paharganj
- Prostate biopsy in Paharganj
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Paharganj
- OIU for stricture urethra in Paharganj
- Laser renal stone surgery in Paharganj
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Paharganj
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Paharganj
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Paharganj
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Paharganj
- Kidney stone treatment in Paharganj
- RIRS surgery in Paharganj
- PCNL surgery in Paharganj
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Paharganj
- TURP surgery in Paharganj
- HoLEP surgery in Paharganj
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Paharganj
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Paharganj
- TURBT surgery in Paharganj
- Prostate cancer treatment in Paharganj
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Paharganj
- Overactive bladder treatment in Paharganj
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Paharganj
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Paharganj
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Paharganj
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Paharganj
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Paharganj
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Paharganj
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Paharganj
- Testicular biopsy in Paharganj
- Micro TESE treatment in Paharganj
- Testicular biopsy in Paharganj
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Paharganj
- Best urologist in Rajouri Garden
- Best andrologist in Rajouri Garden
- Best urology doctor in Rajouri Garden
- Best andrology doctor in Rajouri Garden
- Best andrology treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Best urology treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Urologist treatment specialist in Rajouri Garden
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Rajouri Garden
- Circumcision treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Flexible cystoscopy in Rajouri Garden
- Vasectomy surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Prostate biopsy in Rajouri Garden
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Rajouri Garden
- OIU for stricture urethra in Rajouri Garden
- Laser renal stone surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Rajouri Garden
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Rajouri Garden
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Rajouri Garden
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Kidney stone treatment in Rajouri Garden
- RIRS surgery in Rajouri Garden
- PCNL surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Rajouri Garden
- TURP surgery in Rajouri Garden
- HoLEP surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Rajouri Garden
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Rajouri Garden
- TURBT surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Prostate cancer treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Rajouri Garden
- Overactive bladder treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Rajouri Garden
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Rajouri Garden
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Rajouri Garden
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Rajouri Garden
- Testicular biopsy in Rajouri Garden
- Micro TESE treatment in Rajouri Garden
- Testicular biopsy in Rajouri Garden
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Rajouri Garden
- Best urologist in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best andrologist in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Kanhaiya Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Kanhaiya Nagar
- TURP surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Kanhaiya Nagar
- Best urologist in Shastri Nagar
- Best andrologist in Shastri Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Shastri Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Shastri Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Shastri Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Shastri Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Shastri Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Shastri Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Shastri Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Shastri Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Shastri Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Shastri Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Shastri Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Shastri Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Shastri Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Shastri Nagar
- TURP surgery in Shastri Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Shastri Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Shastri Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Shastri Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Shastri Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Shastri Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Shastri Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Shastri Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Shastri Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Shastri Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Shastri Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Shastri Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Shastri Nagar
- urologist in Rajinder Nagar
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist in Rajinder Nagar
- Best urologist in Rajinder Nagar
- Best andrologist in Rajinder Nagar
- Best urology doctor in Rajinder Nagar
- Best andrology doctor in Rajinder Nagar
- Best andrology treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Best urology treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Urologist treatment specialist in Rajinder Nagar
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Rajinder Nagar
- Circumcision treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Flexible cystoscopy in Rajinder Nagar
- Vasectomy surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Prostate biopsy in Rajinder Nagar
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Rajinder Nagar
- OIU for stricture urethra in Rajinder Nagar
- Laser renal stone surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Rajinder Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Rajinder Nagar
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Rajinder Nagar
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Kidney stone treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- RIRS surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- PCNL surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Rajinder Nagar
- TURP surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- HoLEP surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Rajinder Nagar
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- TURBT surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- Prostate cancer treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Rajinder Nagar
- Overactive bladder treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Rajinder Nagar
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Rajinder Nagar
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Rajinder Nagar
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Rajinder Nagar
- Testicular biopsy in Rajinder Nagar
- Micro TESE treatment in Rajinder Nagar
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Rajinder Nagar
- urologist in Rajendra Place
- Dr Ashish Kumar Urologist in Rajendra Place
- Best urologist in Rajendra Place
- Best andrologist in Rajendra Place
- Best urology doctor in Rajendra Place
- Best andrology doctor in Rajendra Place
- Best andrology treatment in Rajendra Place
- Best urology treatment in Rajendra Place
- Urologist treatment specialist in Rajendra Place
- Andrologist treatment specialist in Rajendra Place
- Circumcision treatment in Rajendra Place
- Flexible cystoscopy in Rajendra Place
- Vasectomy surgery in Rajendra Place
- Prostate biopsy in Rajendra Place
- AV fistula for hemodialysis in Rajendra Place
- OIU for stricture urethra in Rajendra Place
- Laser renal stone surgery in Rajendra Place
- Laparoscopic surgery for kidney in Rajendra Place
- Laparoscopic surgery for ureter in Rajendra Place
- Laparoscopic surgery for bladder in Rajendra Place
- Urinary bladder stone treatment in Rajendra Place
- Kidney stone treatment in Rajendra Place
- RIRS surgery in Rajendra Place
- PCNL surgery in Rajendra Place
- Endoscopic surgery for prostate in Rajendra Place
- TURP surgery in Rajendra Place
- HoLEP surgery in Rajendra Place
- Thulium laser prostatectomy in Rajendra Place
- Urinary bladder cancer treatment in Rajendra Place
- TURBT surgery in Rajendra Place
- Prostate cancer treatment in Rajendra Place
- Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Rajendra Place
- Overactive bladder treatment in Rajendra Place
- Incontinence of urine treatment in Rajendra Place
- Treatment of Male sexual dysfunction in Rajendra Place
- Erectile dysfunction treatment in Rajendra Place
- Premature Ejaculation treatment in Rajendra Place
- Low sex drive treatment for male in Rajendra Place
- Penile prosthesis treatment for male in Rajendra Place
- Evaluation and treatment of male infertility in Rajendra Place
- Testicular biopsy in Rajendra Place
- Micro TESE treatment in Rajendra Place
- Vasectomy Reversal surgery in Rajendra Place
- show more
- show less






